Shipping Container Sizes & Dimensions: A Comprehensive Guide
Article Catalog
1. Standard Container Dimensions (20GP, 40GP, 40HC)
2. How Many Boxes Can Fit in a 20ft/40ft Container (Case Study)
3. How Much Does a 20ft/40ft Container Cost? Hiring or Buying?
4. Dimensions of Other Commonly Seen Containers (20HC, 45HC)
5. Dimensions of Less Common Containers (8GP, 10GP, 10HC, 48HC, 53HC)
6. 4 Factors You Should Consider Whether Hire or Buy Shipping Containers
7. Common Terminologies and Main Markings for Containers
8. Environmental and Multi-use Aspects
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the lifespan of a shipping container?
Q2: What factors should be considered when purchasing a shipping container?
Q3: Suitable Shipping Container Supplier?
Q4: How can shipping containers be loaded and unloaded safely?
Q5: What are the options for dealing with old shipping containers?
Q6: What services do shipping container rental companies typically offer?
1. Standard Container Dimensions (20GP, 40GP, 40HC)
Understanding the standard sizes of shipping containers is crucial for businesses involved in international trade. The most common types are the 20-foot General Purpose (20GP), 40-foot General Purpose (40GP), and the 40-foot High Cube (40HC) containers. Each type has specific dimensions and uses.
(1) 20GP Container
• External Dimensions: 20ft (L) x 8ft (W) x 8.5ft (H)
• Internal Dimensions: 19.4ft (L) x 7.8ft (W) x 7.9ft (H)
• Volume: Approximately 33.2 cubic meters
• Max Gross Weight: 24,000 kg
• Common Uses: Ideal for transporting heavy machinery, tools, and bulk goods due to its compact size.
(2) 40GP Container
• External Dimensions: 40ft (L) x 8ft (W) x 8.5ft (H)
• Internal Dimensions: 39.5ft (L) x 7.8ft (W) x 7.9ft (H)
• Volume: Approximately 67.7 cubic meters
• Max Gross Weight: 30,480 kg
• Common Uses: Suitable for large shipments like furniture, vehicles, and construction materials.
(3) 40HC Container
• External Dimensions: 40ft (L) x 8ft (W) x 9.5ft (H)
• Internal Dimensions: 39.5ft (L) x 7.8ft (W) x 8.9ft (H)
• Volume: Approximately 76.4 cubic meters
• Max Gross Weight: 30,480 kg
• Common Uses: Great for voluminous but lighter cargo such as electronics and clothing.
2. How Many Boxes Can Fit in a 20ft/40ft Container (Case Study)
The number of boxes a container can hold depends on the size of the boxes and how efficiently they are packed.
(1) 20ft Container
Assuming standard-sized boxes (1 cubic meter each):
• 20GP: Around 25-28 boxes
For instance, when transporting electronics, the actual number might be 20-22 due to additional packing materials needed for protection.
(2) 40ft Container
• 40GP: Approximately 55-60 boxes
For furniture, a 40GP container can fit around 55 pieces of standard packed furniture, and efficient packing can increase this number.
3. How Much Does a 20ft/40ft Container Cost? Hiring or Buying?
The cost of containers can vary widely based on condition, age, and location.
(1) 20ft Container
• Buying: $2,000 - $3,000, depending on whether it's new or used, and market conditions.
• Hiring: $75 - $100 per month, usually including basic maintenance.
In different regions:
• East Coast, USA: Higher prices, around $3,000 to buy and $100 per month to hire.
• Midwest, USA: Lower prices, around $2,500 to buy and $75 per month to hire.
(2) 40ft Container
• Buying: $3,500 - $4,500
• Hiring: $100 - $150 per month
(3) Deciding whether to hire or buy depends on your long-term needs and budget. Here’s a comparison:
• Long-term (over 3 years): Buying is more cost-effective.
• Short-term (under 1 year): Hiring is more economical.
4. Dimensions of Other Commonly Seen Containers (20HC, 45HC)
(1) 20HC Container
• External Dimensions: 20ft (L) x 8ft (W) x 9.5ft (H)
• Internal Dimensions: 19.4ft (L) x 7.8ft (W) x 8.9ft (H)
• Volume: Approximately 37.4 cubic meters
• Max Gross Weight: 24,000 kg
• Common Uses: Useful for cargo requiring more vertical space, such as tall equipment.
(2) 45HC Container
• External Dimensions: 45ft (L) x 8ft (W) x 9.5ft (H)
• Internal Dimensions: 44.5ft (L) x 7.8ft (W) x 8.9ft (H)
• Volume: Approximately 86 cubic meters
• Max Gross Weight: 32,500 kg
• Common Uses: Ideal for large, voluminous items like large appliances and bulk goods.
5. Dimensions of Less Common Containers (8GP, 10GP, 10HC, 48HC, 53HC)
(1) 8GP Container
• External Dimensions: 8ft (L) x 8ft (W) x 8.5ft (H)
• Internal Dimensions: 7.7ft (L) x 7.8ft (W) x 7.9ft (H)
• Volume: Approximately 15 cubic meters
• Max Gross Weight: 10,000 kg
• Common Uses: Suitable for smaller shipments or limited storage space needs.
(2) 10GP Container
• External Dimensions: 10ft (L) x 8ft (W) x 8.5ft (H)
• Internal Dimensions: 9.7ft (L) x 7.8ft (W) x 7.9ft (H)
• Volume: Approximately 16 cubic meters
• Max Gross Weight: 10,160 kg
• Common Uses: Perfect for smaller loads and can be used as portable storage units.
(3) 10HC Container
• External Dimensions: 10ft (L) x 8ft (W) x 9.5ft (H)
• Internal Dimensions: 9.7ft (L) x 7.8ft (W) x 8.9ft (H)
• Volume: Approximately 19 cubic meters
• Max Gross Weight: 10,160 kg
• Common Uses: Suitable for cargo requiring extra height, such as certain machinery.
(4) 48HC Container
• External Dimensions: 48ft (L) x 8ft (W) x 9.5ft (H)
• Internal Dimensions: 47.6ft (L) x 7.8ft (W) x 8.9ft (H)
• Volume: Approximately 96 cubic meters
• Max Gross Weight: 32,500 kg
• Common Uses: Ideal for very large shipments, including oversized industrial equipment.
(5) 53HC Container
• External Dimensions: 53ft (L) x 8.5ft (W) x 9.5ft (H)
• Internal Dimensions: 52.6ft (L) x 8.3ft (W) x 8.9ft (H)
• Volume: Approximately 111 cubic meters
• Max Gross Weight: 32,500 kg
• Common Uses: Common in North America for domestic transportation of large quantities of goods.
6. 4 Factors You Should Consider Whether Hire or Buy Shipping Containers
(1) Duration of Use: Long-term projects (over 3 years) might benefit more from buying, while short-term needs (less than 1 year) might be more cost-effective to hire.
(2) Budget: Initial capital outlay versus ongoing rental costs. Buying requires a larger upfront cost, while hiring spreads out the cost over time.
(3) Maintenance: Owned containers require regular maintenance, whereas hired containers typically include this in the rental fee.
(4) Flexibility: Hiring offers flexibility to scale up or down quickly as needs change, and it eliminates the hassle of reselling used containers.
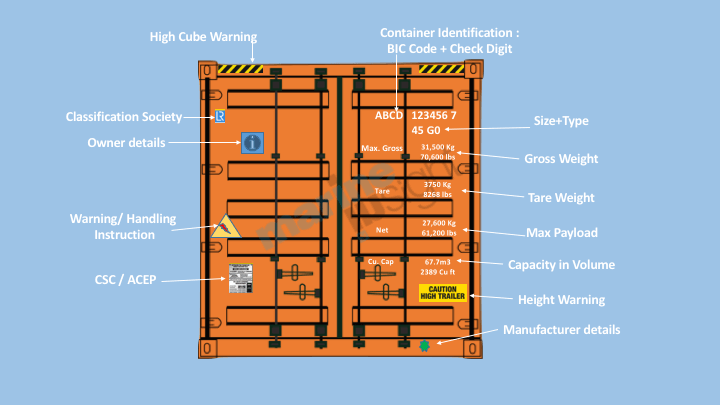
7. Common Terminologies and Main Markings for Containers
Understanding container terminologies and markings can streamline logistics and ensure compliance.
Common Terminologies
• GP: General Purpose
• HC: High Cube
• TEU: Twenty-foot Equivalent Unit
• FEU: Forty-foot Equivalent Unit
• Reefer: Refrigerated Container
• Open Top: Containers with a removable top for oversized cargo
Main Markings
• Container ID (BIC Code + Check Digit)
• Size + Type
• ISO Code
• Max. Gross Weight
• Tare Weight
• Max. Payload
• Capacity in Volume
• Height Warning
• Manufacturer Details
• High Cube Warning
• Classification Society
• Owner Details
• Warning/Handling Instruction
• CSC Plate, ACEP, or other Certificates• Container Number: Unique identifier for tracking and logistics purposes
8. Environmental and Multi-use Aspects
Containers are not only used for shipping but also repurposed for other uses like temporary offices, housing, and retail spaces, contributing to sustainability by promoting reuse.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the lifespan of a shipping container?
A: The lifespan of a shipping container depends on several factors including usage frequency, environmental conditions, and maintenance. Generally, the expected lifespan of a new container is around 10 to 12 years, while second-hand containers may have a slightly shorter lifespan.
Q2: What factors should be considered when purchasing a shipping container?
A: When purchasing a shipping container, factors to consider include capacity, quality, maintenance costs, and the ability to accommodate specific types of cargo. Additionally, it's important to inspect the structural integrity and exterior condition of the container before purchase to ensure it meets requirements.
Q3: Suitable Shipping Container Supplier?
(1) Most shipping containers (about 95%) are made in China, and you can find the appropriate container suppliers at a good price.
(2) The worldwide largest container manufacturers are located in China. CIMC (China International Marine Containers Co., Ltd), Singamas Group, Shanghai Universal Logistics Equipment Co., Ltd, and CXIC Group Containers Company Limited are the top 4.
(3) Particularly, CIMC supplies half of the world’s container manufacturing.
Q4: How can shipping containers be loaded and unloaded safely?
A: Loading and unloading shipping containers require specialized equipment and techniques. It's advisable to seek assistance from experienced logistics companies or professional teams to ensure safe operations and minimize the risk of injury to both goods and personnel.
Q5: What are the options for dealing with old shipping containers?
A: Old shipping containers can be repurposed or recycled. They can be converted into temporary housing, offices, or storage units, or sold to container dealers or recycling companies for a certain value return.
Q6: What services do shipping container rental companies typically offer?
A: Shipping container rental companies typically offer services such as container rental, transportation, installation, and maintenance. Some companies also provide customized container solutions to meet specific customer needs and requirements.

