LCL vs. FCL: Choosing the Right Shipping Method
Article Catalog
2. FCL vs LCL | Most Commonly Seen Differences (Charts Explained)
3. What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of FCL and LCL?
4. FCL Price & LCL Sea Freight (Case Study)
5. Document and Operation Process Differences between FCL and LCL
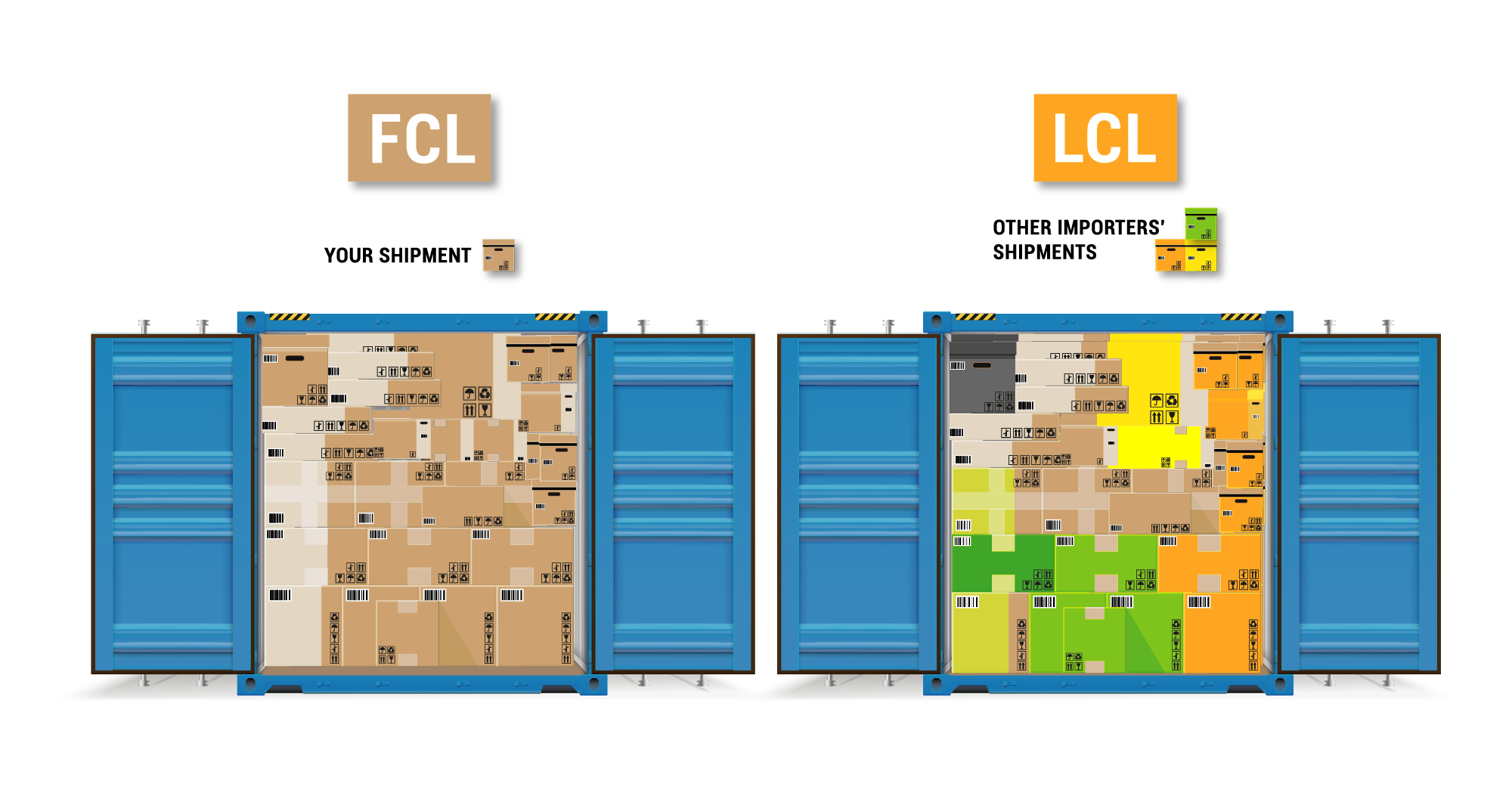
In international trade, understanding shipping methods is crucial for efficient logistics and cost management. Two common shipping methods are LCL (Less than Container Load) and FCL (Full Container Load).
LCL shipment: means your goods share a container with other shipments,
FCL shipping: involves renting an entire container for your own use.
Each method has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and the right choice depends on your specific needs.
Note: 40HQ = 40 high cube container; 1 CBM = 1 Cubic Meter.
2. FCL vs LCL | Most Commonly Seen Differences (Charts Explained)
Understanding the differences between FCL and LCL can help you choose the best option for your business. Here are the most commonly seen differences:
| Aspect | FCL (Full Container Load) | LCL (Less than Container Load) |
| Cost | Higher cost but potentially lower per unit | Lower cost but higher per unit |
| Volume Shipments | 1.Suitable for higher volume 2.Best for cargo with a volume of 15 CBM or more. 3.20GP –28 CBM; 40 GP – 58 CBM; 40 HQ – 68 CBM. |
1.Ideal for smaller shipments 2.Very suitable for less than 15 CBM volumes of cargo. 3.The min. volume is 1-3CBM. Crago less than 1CBM is charged by 1 CBM. |
| Risk of Damage | Lower risk of damage | Higher risk due to handling |
| Speed | Faster transit times | Slower due to consolidation |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible |
| Unloading Sorting | Easier unloading and sorting | More complex unloading and sorting |
| Note | 1. Recommend to consider air freight when your cargo is less than 1 CBM and weighs less than 200kg (150kg during peak season). 2. Recommend to consider FCL when your cargo uses 10+ standard pallets. |
|
Cargo Weight
| LCL | FCL |
| Max. weight per CBM - 1 ton (1,000 kg). | 20 GP – 18.6 tons; 40 GP & 40 HQ – 28.6 tons. |
| If exceeded, it’s charged by gross weight. | Some nations have their max. allowable weight. |
| For example: when 1,300 kg cargo is loaded in 1 CBM, it’s charged 1.3 CBM. | For example: in the US, 20 GP – 17 tons; 40 GP and 40 HQ – 21 tons. |
| Note: It’s required to move the rest cargo to a different container if your FCL exceeds the max. weight regulated by nations. | |
Ocean Freight
Many people may think they need to choose LCL shipping when they load less than a full container of cargo. It’s not right. Here we should pay attention to a cargo volume range of "13-17 CBM" where we can consider both LCL and FCL. Why?
If your product fills 17 cubic meters, choosing LCL means paying more for sorting labor at the port. This is more expensive than using ocean freight and will increase your overall expenses. In this case, it’s costly for you to choose a full 20ft container (28 CBM of cargo loading at most).
LCL: Cheaper to import cargo<15 CBM.
FCL: Cheaper to import cargo ≥15 CBM.
Note: LCL shipping rates tend to be more stable. And FCL price per CBM is lower than LCL’s.
3. What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of FCL and LCL?
Advantages of FCL:
1. Lower Risk: You have a reduced risk of damage, theft, or loss because your goods are not mixed with others.
2. Faster Shipping: Since the container is only for your goods, FCL shipments typically have quicker transit times.
3.FCL is cost-effective for big shipments because larger shipments are cheaper due to the volume of goods being shipped.
Disadvantages of FCL:
1. Higher Initial Cost: Renting a full container can be expensive if you don't have enough goods to fill it.
2. Less Flexibility: FCL is less flexible when shipping smaller quantities.
Advantages of LCL:
1. Cost-Effective for Smaller Loads: Ideal for businesses that don’t need an entire container.
2. Flexible: Easier to ship smaller quantities, providing flexibility.
Disadvantages of LCL:
1. Higher Risk of Damage: More handling and sharing space with other shipments increase the risk.
2. Slower Transit: Consolidation and deconsolidation add time to the shipping process.
3. One mistake of a consignment will cause non-release of the whole container and further affect the timely transport.
4. FCL Price & LCL Sea Freight (Case Study)
The FCL price covers the cost of shipping a full container load. It also includes additional charges such as fuel fees, exchange rate adjustments, and port expenses.
Shipping companies are increasing their prices because fuel costs have gone up and currency values have changed. However, there is no fixed rate for these additional charges. You’d better ask freight forwarders for the latest specific fees. In addition, ocean freight “all-in” (all-inclusive) covers all possible extra fees as mentioned above.
The LCL cost mainly includes ocean freight, warehousing expenses, grouping & ungrouping charges, plus other fees. Calculate LCL sea freight based on the volume used in a shared container. Lower than grouping and ungrouping charges at warehouses that involve a large amount of manpower and infrastructure.
The shipping companies determine the sea freight, and it changes in real time. Particularly, the recent sea freight quotation is valid for about 1 week, changing quickly.
For example, if you ship bulk cargo from Ningbo to Los Angeles port, LCL sea freight is around $70/CBM. Shipping a lot of cargo from Ningbo to Los Angeles port? The FCL shipping rates are $1500 per container for 20GP and $1600 per container for 40HQ. Again, remember 20GP = 28 CBM, and 40HQ = 68 CBM.
The above is for reference only. Note that sea freight is higher in the peak season (August to October every year). Airline tickets are cheaper during the off-peak season, with discounts of 50-60%. However, prices increase significantly during the peak season.
We are about to ship 100 boxes of goods by sea. Box size: 25x20x20cm; box net weight: 13kg; box gross weight: 15kg.
The calculation standard is W/M, Class 10, and basic freight is $200 per FT (freight ton). The port expense charges 10% of the basic freight. And the fuel fee is $10 per FT. So, what’s the total sea freight?
Step 1 – Basic Freight
· W (Weight) = 15kg = 0.015tons
· M (Measurement or Volume) = (0.25×0.2×0.2) = 0.01 m³
Choose the larger W for calculation. Basic Freight = 0.015x100x200 = $300
Step 2 – Surcharges
· Fuel Fees = 0.015x100x10 = $15
· Port Expense = 300×10% = $30
Total Surcharges = Fuel Fees + Port Expense = $45
Step 3 – Total Sea Freight
Basic Freight + Surcharges = $300 + $45 = $345
Sea Freight Calculting Tips:
1. Compare W (weight) and M (measurement), and then use the larger one as the calculating unit.
2. Total sea freight = W/M x (basic freight + surcharges)
5. Document and Operation Process Differences between FCL and LCL
Documentation:
FCL Shipping:
- Requires a Bill of Lading specifically for your container.
- Fewer documents since there’s no need to manage shared shipments.
LCL Shipping:
- Requires a Bill of Lading that lists all shared shipments.
- Additional paperwork for consolidation and deconsolidation.
Operation Process
FCL Operation:
1. The supplier receives the container.
2. Supplier loads the container.
3. They seal the container and transport it directly to the port.
4.The carrier ships and delivers the container to the consignee without further handling.
LCL Operation:
1.A warehouse receives goods.
2. We consolidate goods with other shipments.
3.Transport the shared container to the port.
4.The container is shipping.
5.At the destination, workers deconsolidate and deliver goods to respective consignees.
Choosing between FCL and LCL depends on your shipment volume, budget, and risk tolerance. For higher volume shipments, FCL shipping offers a cost-effective, faster, and safer option. For smaller loads, LCL shipping provides flexibility and lower initial costs but comes with higher risks and longer transit times. Understanding these differences can help you make informed decisions to optimize your international trade logistics.
Q1: How do I choose between FCL and LCL?
A: Consider the volume of goods, cost, transit time, and risk factors. FCL is ideal for larger shipments, while LCL is suitable for smaller volumes.
Q2: What is the transit time difference between FCL and LCL?
A: FCL usually has a shorter transit time as it involves direct shipping, whereas LCL takes longer due to consolidation and deconsolidation processes.
Q3: What are the risks associated with LCL shipping?
A: A: LCL has a higher risk of damage, theft, or loss because of increased handling and mixing with other shipments.
Q4: Is FCL more expensive than LCL?
A: FCL can be more expensive for small shipments but becomes more cost-effective for larger volumes.
💡 Contact us now and let Eason Electronic become your trusted partner in realizing your business vision.

